Search Engine Optimization(SEO), is the process of optimizing your web pages to improve its visibility on search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo. A strong SEO strategy helps achieve business goals by driving organic traffic and building brand awareness.
In this article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about SEO, from its components to actionable tips you can implement to improve your website’s performance.
What is SEO?
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the practice of enhancing a website to rank higher on search engine results pages (SERPs). The aim is to attract more organic traffic by meeting the needs of users searching for specific information.
SEO can be thought of as a bridge between search engines and users. It ensures that your content is discoverable, relevant, and authoritative.
What Are The Benefits of SEO For Your Business
In today’s competitive digital landscape, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is crucial for businesses of all sizes. An effective SEO strategy can drive remarkable growth by enhancing your website’s online visibility, increasing organic traffic, and improving user engagement. Let’s dive deeper into the benefits of SEO and why it’s crucial for your business.
1. Increases Organic Website Traffic
- Ranking higher on search engine results pages (SERPs) increases your website’s visibility to potential customers.
- By targeting high-volume keywords relevant to your niche, SEO ensures you attract users actively searching for your products or services.
- Unlike paid ads, organic traffic from SEO is free, making it a cost-effective way to grow your audience.
2. Improves Brand Visibility and Recognition
- SEO optimizes your content to appear in front of your target audience when they search for related terms.
- Frequent appearances at the top of Google search results build brand awareness and help establish authority in your industry.
- Through keyword optimization and local SEO efforts, even small businesses can achieve significant visibility.
3. Builds Authority, Credibility, and Trust
- Websites that rank higher are perceived as more credible and trustworthy by users.
- By implementing white-hat SEO techniques, such as creating high-quality content and earning backlinks, your business can enhance its online reputation.
- A strong domain authority (DA) achieved through consistent SEO practices fosters long-term trust.
4. Enhances User Experience (UX)
- SEO goes beyond keywords; it involves improving your website’s structure, speed, and navigation.
- A mobile-friendly, fast-loading website optimized for core web vitals keeps users engaged and reduces bounce rates.
- By addressing technical SEO issues, you ensure a seamless browsing experience that boosts user satisfaction.
5. Provides Sustainable and Long-Term Results
- SEO offers long-term benefits by maintaining a steady flow of organic traffic.
- Unlike paid campaigns, which stop delivering leads as soon as your budget ends, a well-optimized website keeps ranking on search engines with regular updates.
- Strategic SEO efforts compound over time, delivering consistent results and growth.
6. Drives Local Business Growth
- Local SEO strategies help businesses rank in searches for location-specific queries, such as “best coffee shop near me” or “plumbing services in [city].”
- Optimizing your Google My Business profile enhances your visibility in local map packs, driving foot traffic to your business.
- By focusing on location-based keywords, you can dominate your local market and connect with nearby customers.
Types Of SEO And How To Use Them
SEO can be divided into three primary categories: On-Page SEO, Off-Page SEO, and Technical SEO. Understanding these pillars is crucial to developing a good strategy.
1. On-Page SEO
Focuses on optimizing individual web pages to rank higher on search engines.
Key Strategies:
- Keyword Optimization: Research and include relevant keywords in titles, headers, and content.
- Meta Tags: Write compelling meta titles and descriptions.
- URL Structure: Use clean and descriptive URLs.
- Content Quality: Provide valuable, original, and engaging content.
- Internal Linking: Link to other relevant pages on your website.
- Image Optimization: Use descriptive file names and alt tags for images.
How to Use:
- Regularly update and optimize existing pages with new keywords and trends.
- Use tools like Yoast SEO for guidance on improving on-page SEO.
2. Off-Page SEO
Enhances your website’s authority and reputation outside your site.
Key Strategies:
- Backlink Building: Get high-quality backlinks from reputable websites.
- Social Media Marketing: Share content on social platforms to increase traffic.
- Guest Posting: Publish articles on other websites to gain visibility.
- Influencer Outreach: Collaborate with influencers to promote your content.
How to Use:
- Network with industry leaders and participate in forums.
- Use tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush to identify backlink opportunities.
3. Technical SEO
Involves optimizing the technical aspects of your website for better performance and crawling.
Key Strategies:
- Website Speed: Optimize loading times using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights.
- Mobile-Friendliness: Ensure your site is responsive on all devices.
- XML Sitemaps: Create and submit sitemaps to search engines.
- Structured Data: Use schema markup to enhance search visibility.
- Secure Connection: Implement HTTPS for security.
How to Use:
- Perform regular technical audits using tools like Screaming Frog or Google Search Console.
- Fix broken links and resolve errors promptly.
4. Local SEO
Optimizes your site for local search queries, ideal for businesses targeting specific areas.
Key Strategies:
- Google My Business (GMB): Set up and optimize your GMB profile.
- Local Keywords: Use geo-targeted keywords like “Digital Marketing in Nairobi.”
- NAP Consistency: Ensure Name, Address, and Phone information is accurate across platforms.
- Local Reviews: Encourage customer reviews on Google and Yelp.
How to Use:
- Regularly update your GMB listing.
- Build local backlinks and collaborate with local organizations.
5. Content SEO
Focuses on creating and optimizing content to attract search engine traffic.
Key Strategies:
- Content Research: Identify trending topics and user intent.
- Content Formatting: Use headings, bullet points, and visuals for readability.
- Evergreen Content: Create timeless, high-value content.
- Multimedia Content: Incorporate videos, infographics, and images.
How to Use:
- Develop a content calendar to ensure regular updates.
- Use tools like Google Trends and AnswerThePublic for content ideas.
6. E-Commerce SEO
Specializes in optimizing online stores to improve product visibility and sales.
Key Strategies:
- Product Descriptions: Write unique and keyword-rich descriptions.
- Category Pages: Optimize category pages with relevant keywords.
- Product Reviews: Encourage customers to leave reviews.
- Site Navigation: Use a clear structure to improve user experience.
How to Use:
- Use platforms like Shopify or WooCommerce for built-in SEO features.
- Optimize product images and include alt text.
7. International SEO
Optimizes your website for global audiences in different regions and languages.
Key Strategies:
- Hreflang Tags: Indicate language and region settings to search engines.
- Localized Content: Tailor content for different audiences.
- Global Keywords: Use region-specific keywords.
- Country-Specific Domains: Use domains like .uk, .fr, or .ke for specific countries.
How to Use:
- Research target markets and their search behaviors.
- Use tools like SEMrush or Google Keyword Planner for international keyword research.
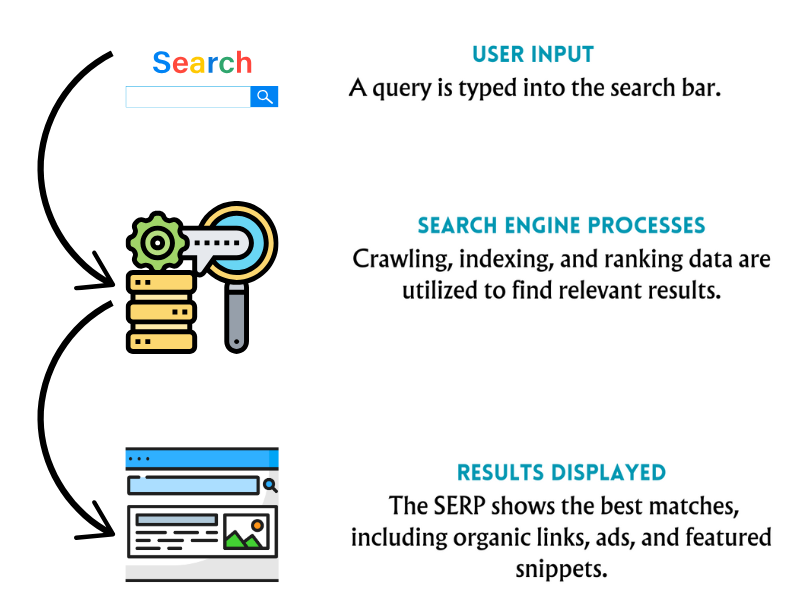
How Do Search Engines Work?
Search engines are complex systems designed to find, organize, and display relevant content from the internet in response to user queries. They operate in three main stages: crawling, indexing, and ranking. Here’s a breakdown of how they work:
1. Crawling
Search engines start by discovering new and updated web pages.
Key Components:
- Crawlers (Spiders/Bots): Automated programs that visit web pages and follow links to other pages.
- Discovering Content: Crawlers find content through links, sitemaps, and direct submissions (e.g., Google Search Console).
- Page Content Analysis: Crawlers read the text, metadata, and HTML of each page.
Challenges:
- Pages with restricted access (e.g., password-protected or noindex tags).
- Duplicate content and broken links.
2. Indexing
Once a page is crawled, its content is analyzed and stored in the search engine’s database (index).
Key Components:
- Content Understanding: Search engines evaluate the page’s topic, keywords, images, and multimedia.
- Structured Data: Schema markup helps search engines understand specific elements, like reviews or events.
- Content Quality: Pages with high-quality, relevant, and original content are prioritized in the index.
Challenges:
- Pages with poor-quality content or non-standard code may be excluded from the index.
3. Ranking
When a user searches for something, the search engine retrieves the most relevant results from its index.
Key Components:
- Relevance: How closely the content matches the search query.
- Authority: Determined by backlinks and the credibility of the content source.
- User Experience: Factors like page load speed, mobile-friendliness, and usability influence rankings.
- Freshness: Recent and updated content may rank higher for time-sensitive queries.
Search Engine Algorithms:
- Algorithms evaluate hundreds of ranking factors to determine the order of results.
- Factors include keyword usage, user intent, and engagement metrics (e.g., click-through rates).
4. Displaying Results
Search engines present results on the Search Engine Results Page (SERP).
Features:
- Organic Results: Unpaid results ranked based on relevance and quality.
- Paid Results: Ads displayed based on a bidding system (e.g., Google Ads).
- Rich Snippets: Enhanced results with additional information (e.g., ratings, FAQs).
- Knowledge Panels: Summarized information about a topic.
Simplified Workflow
What is Keyword Research?
Keyword research is the process of identifying the words and phrases people enter into search engines to find information, products or services. Keyword research helps to target the right audience and drive organic traffic to your website.
Why Is Keyword Research Important?
- Improves SEO: Helps optimize your website and content for terms that your audience is searching for.
- Increases Visibility: Targets high-volume, low-competition keywords to improve rankings on search engines.
- Understands Audience Intent: Reveals what your audience is looking for and their needs.
- Drives Conversions: Targets keywords aligned with purchase intent or problem-solving queries.
Types of Keywords
- Short-Tail Keywords:
- 1-2 words, e.g., “digital marketing.”
- High search volume but competitive.
- Long-Tail Keywords:
- 3 or more words, e.g., “digital marketing strategies for small businesses.”
- Lower search volume but highly specific and less competitive.
- Transactional Keywords:
- Indicate buying intent, e.g., “buy video editing software online.”
- Informational Keywords:
- Indicate a search for knowledge, e.g., “how to use Canva for graphic design.”
- Navigational Keywords:
- Indicate brand or site-specific searches, e.g., “Bluehost login page.”
Steps in Keyword Research
1. Brainstorm Topics
List broad topics related to your business, industry, or content goals.
2. Use Keyword Research Tools
Leverage tools to find keywords, their search volume, competition, and trends. Examples:
- Google Keyword Planner
- SEMrush
- Ahrefs
- Ubersuggest
- AnswerThePublic
3. Analyze Search Intent
Understand the purpose behind the keyword:
- Informational: Research or learning.
- Navigational: Finding a specific brand or site.
- Transactional: Making a purchase.
4. Evaluate Keyword Metrics
Focus on:
- Search Volume: The number of times a keyword is searched.
- Keyword Difficulty (KD): How hard it is to rank for a keyword.
- Cost-Per-Click (CPC): Useful for paid campaigns to determine advertising costs.
5. Prioritize Keywords
Select a mix of short-tail and long-tail keywords, targeting high-relevance and manageable competition.
Best Practices for Keyword Research
- Think Like Your Audience: Consider what they might search for.
- Analyze Competitors: Check what keywords they rank for using tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs.
- Focus on Long-Tail Keywords: They often convert better due to specificity.
- Update Regularly: Trends and search behavior evolve; revisit your keywords periodically.
Content Optimization Strategies
Content Optimization Strategies are techniques used to improve the visibility, relevance, and performance of your content on search engines and across digital platforms. Effective optimization can help your content rank higher, attract the right audience, and drive conversions. Here are some of the strategies you can implement for best results.
1. Perform Thorough Keyword Research
- Identify Relevant Keywords: Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, or Ahrefs to find keywords with good search volume and low competition.
- Focus on Long-Tail Keywords: Target specific queries to attract a niche audience and improve conversion rates.
- Match Search Intent: Align content with informational, transactional, or navigational intent.
2. Optimize On-Page SEO
- Title Tags: Include primary keywords and keep them under 60 characters.
- Meta Descriptions: Write compelling summaries with keywords; keep them under 160 characters.
- Header Tags (H1, H2, H3): Use headings to structure your content and include keywords naturally.
- URL Structure: Create clean, keyword-rich URLs (e.g.,
yourwebsite.com/content-optimization-strategies). - Internal Linking: Link to related content on your site to improve navigation and boost SEO.
3. Focus on High-Quality, Engaging Content
- Solve Problems: Address the pain points and queries of your audience.
- Be Comprehensive: Provide detailed, accurate, and actionable information.
- Visuals: Use images, infographics, and videos to break up text and engage readers.
- Readability: Write in a clear, conversational tone with short paragraphs and bullet points.
4. Mobile Optimization
- Ensure your website is responsive and loads quickly on mobile devices.
- Test usability on different screen sizes and browsers to improve the user experience.
5. Leverage Multimedia Content
- Add videos, infographics, and podcasts to make your content more engaging.
- Optimize multimedia elements with descriptive file names, alt text, and captions.
What Are The Tools Used For SEO?
Free Tools
- Google Analytics: Tracks website traffic and user behavior.
- Google Search Console: Monitors your website’s indexing and performance.
- Yoast SEO: A WordPress plugin for on-page SEO optimization.
Paid Tools
- SEMrush: Comprehensive SEO and keyword research tool.
- Ahrefs: Backlink analysis and keyword tracking.
- Moz Pro: Keyword research and site audits.
Measuring And Tracking SEO Performance
Key Metrics to Track
- Organic Traffic: Monitor the number of visitors from search engines.
- Bounce Rate: Identify pages that cause users to leave.
- Conversion Rate: Measure how many visitors take desired actions.
Regular SEO Audits
Conduct periodic audits to identify issues and areas for improvement. Tools like Screaming Frog and Sitebulb can automate this process.
Conclusion
SEO is a continuous journey, not a one-time effort. By understanding its principles and staying updated with trends, you can build a robust strategy that delivers consistent results. Start implementing these best practices today to drive more organic traffic and achieve your digital marketing goals.

